Officially, the ngudlukanta – also known as the desert rat-kangaroo (Caloprymnus campestris) – is one of the many small Australian mammals lost to cats and foxes, but all hope is not gone. If ngudlukantas do indeed live, a project exploring the mechanics of their jaws could be key to finding and protecting the survivors.
ADVERTISEMENT
The plausibility of the undetected survival of a species varies with many factors. You don’t need to be a wild-eyed conspiracy theorist to think a nocturnal creature smaller than a rabbit whose home range is among the most sparsely inhabited places on Earth has a shot at survival. Cameras and spotlighting walks failed to substantiate reports of ngudlukanta sightings – however, the search region is a vast area of central Australia. If there is any chance the ngudlukanta lives, our best chance to find them is to narrow the habitat they once favored, and their diet is probably the best guide.
This is where the new research comes in. The team examined the jaws and teeth of the handful of museum fossils that survive and compared them to the ngudlukanta’s nearest relatives.
Desert rat-kangaroos are (or were) much more kangaroos than rodents: They’re marsupials and members of the potoroidae, along with several living bettong and potoroo species. It’s only their size and nocturnal lifestyle that led European naturalists to put the rat in their name. They’re no relation to the North American kangaroo rat.
The team collaborated with The University of New England’s Professor Stephen Wroe, who has pioneered the science of calculating the bite force of different animals using a combination of fossils, computer models and benchmarking against species we can test. He’s most famous for comparing the bites of megalodon and T. rex, (as well as explaining Neanderthal’s faces, but he works at the small end of the scale as well.
“Rat-kangaroos, like bettongs and potoroos, are an ideal group of animals for testing skull biomechanics because they each have different shaped skulls and specialize on very different food groups,” lead author Dr Rex Mitchell of Flinders University said in a statement.
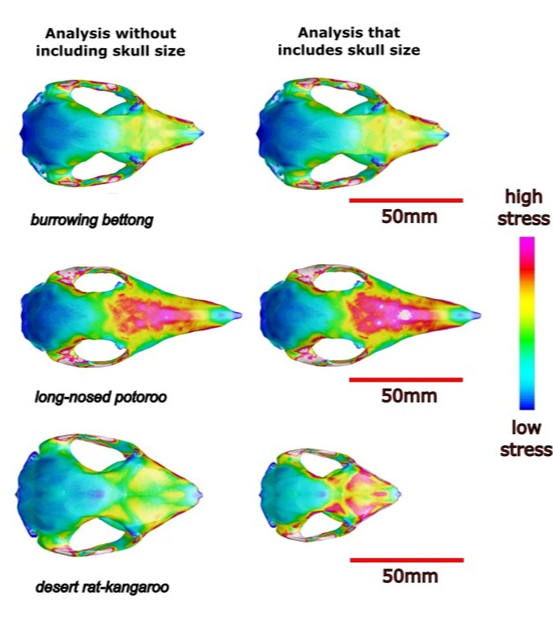
A comparison of the desert rat-kangaroo and its closest relative. The shape suggests greater strength, but note the size.
Image Credit: Mitchell et al
The team found that ngudlukantas’ diet was more restricted than previously thought.
ADVERTISEMENT
“We were surprised to find the heftier skull of the desert rat-kangaroo isn’t necessarily adapted for biting into harder foods. When we included the animal’s smaller size into the analysis, the robust features of the desert rat-kangaroo’s skull were only found to be effective enough to handle eating a softer range of foods,” Mitchell said.
Previous reconstructions of the ngudlukantas’ capability noted that its jaw was more robust in shape than relatives like the northern bettong, but forgot sometimes size does matter. Taking this into account, the team realized the ngudlukanta’s bite force was proportionally smaller, more like the delicate long-nosed potoroo, which feeds on fungi. This information could focus future search missions.
“It is plausible that a small, nocturnal species could be evading detection in the vast inland desert. In fact, this species was previously a resurrected ‘Lazarus’ species after its rediscovery in the 1930s,” said senior author, Flinders’ Dr Vera Weisbecker. Australia’s vast dry inlands host a few survivors prematurely declared extinct, but coming back twice would be a truly remarkable feat.
Besides the arrival of predators ngudlukantas had no time to adapt to, additional pressures were placed by the spread of fast-breeding rabbits, cattle, and sheep. Changes to fire regimes didn’t help either. Nevertheless, the ngudlukanta’s range extended into areas too dry in most years for predators or competitors, and perhaps they’re still hopping there.
ADVERTISEMENT
The study is published open access in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
Source Link: Bite Mechanics Could Help Reveal If Rumors Of Rat-Kangaroo’s Death Are Exaggerated