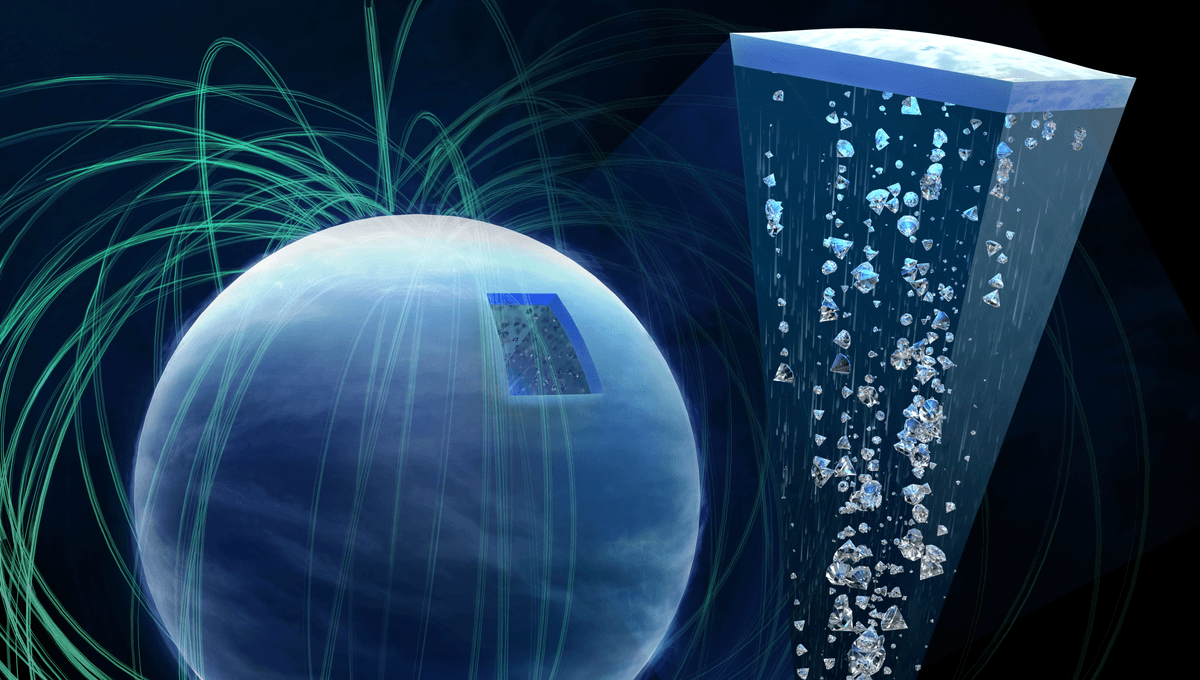
Diamonds on Earth are pretty rare, despite being a girl’s best friend. But on ice giant planets like Uranus and Neptune, it is expected that diamonds rain down through the atmosphere. Now, lab experiments suggest that sparkly precipitation happens at lower temperatures and pressure than previously thought, making it more common not just in the solar system, but also elsewhere in the universe. It might also play a role in influencing the magnetic fields of these planets.
We can’t fly into the deep layers of the atmosphere where the diamonds form, but we can create similar conditions in the lab. Using diamond anvils, researchers subjected a film made of polystyrene to incredible pressure. They then hit the film with high-energy X-rays that heated the sample to more than 2,200 degrees Celsius (3992 degrees Fahrenheit) and diamonds began to form.
The team was also able to experiment on longer timescales, as well as investigate how carbon compounds reacted in the presence of oxygen. They saw that it was possible to create these diamonds at lower temperatures and pressures, meaning that they spend more time in the atmosphere of the planet, before falling deeper into it.
And it’s not just about the precipitation. The magnetic fields of Uranus and Neptune are not symmetric like Earth’s own and is believed to be created by conductive layers deep within the planet. The presence of diamonds falling through those layers, carrying gas and ice as they descend, could stir them up, creating currents and potentially even driving the magnetic fields.
“‘Diamond rain’ on icy planets presents us with an intriguing puzzle to solve,” lead author and SLAC scientist Mungo Frost said in a statement. “It provides an internal source of heating and transports carbon deeper into the planet, which could have a significant impact on their properties and composition. It might kick off movements within the conductive ices found on these planets, influencing the generation of their magnetic fields.”
Since the study shows that lower temperatures and pressures are needed to create these diamond rains, it means that smaller worlds – so-called mini-Neptunes – may likely have diamonds falling into their depths. Understanding our ice giant neighbors with direct observations and in the lab opens the door to understanding countless worlds out there.
“This groundbreaking discovery not only deepens our knowledge of our local icy planets, but also holds implications for understanding similar processes in exoplanets beyond our solar system,” said Siegfried Glenzer, director of SLAC’s High Energy Density division.
The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
Source Link: Diamonds May Rain Across The Universe More Often Than Than We Thought