Something fishy has unfolded in the Gulf of Panama. For the first time in recorded history, the annual restock of cold, nutrient-rich waters failed to emerge off Panama’s Pacific coastline. The cause is not totally clear, but the impact could be profound.
Every year for four decades, researchers have noted how the waters in the Gulf of Panama become enriched with cold, nutrient-rich waters that arise from the depths of the ocean to the surface. In turn, life is replenished and the cycle renews itself.
Known as upwelling, this annual rite of the oceans always occurs during the dry months from December to April – until 2025 broke the pattern.
The freak anomaly was detected by scientists at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, who compared it to a vast bank of historic data. They drew on 40 years of satellite records, coastal temperature logs, and even ship-based measurements from the research vessel Eugen Seibold.
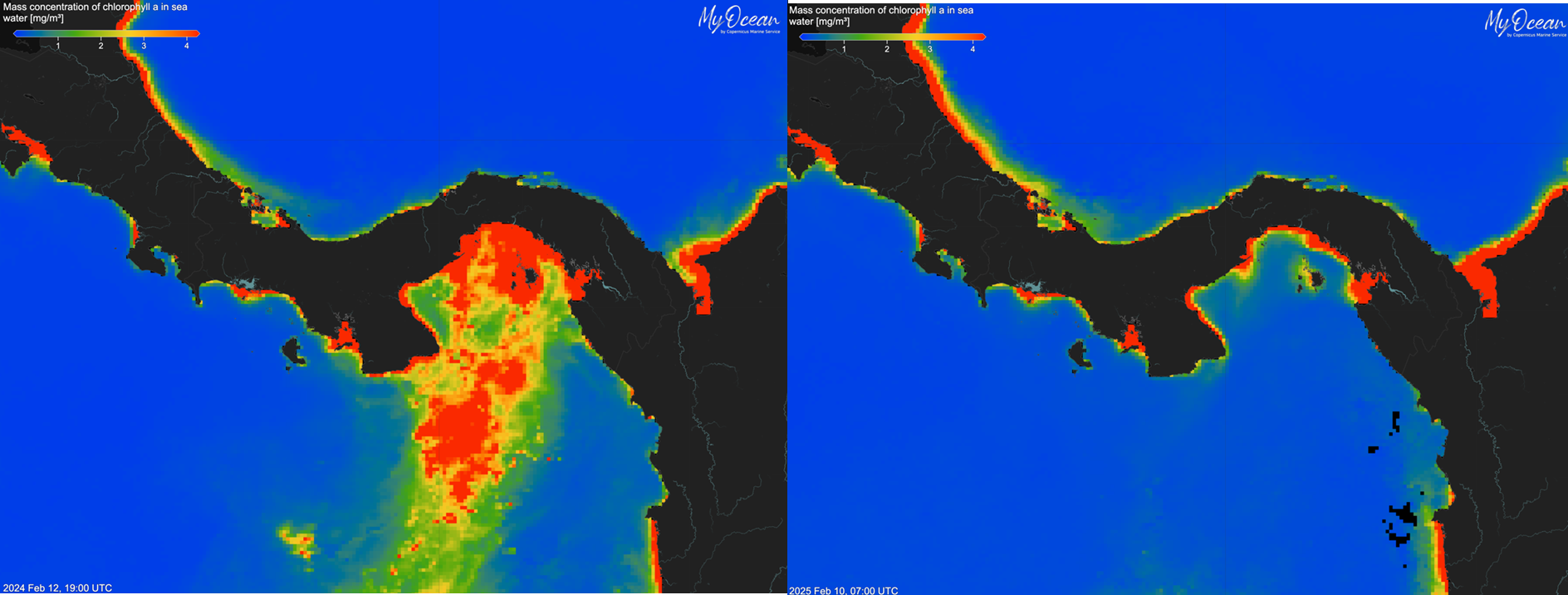
Map of the Gulf of Panama showing high chlorophyll concentrations in February 2024 (left) compared to extremely low chlorophyll concentrations in February 2025 (right).
Image credit: Aaron O’Dea (CC BY)
In a typical year, these datasets show a reliable seasonal signal of upwelling. Most vividly, scientists see a bloom of chlorophyll in the Gulf, a clear indication that life is thriving and the oceanic food webs have plenty of fuel.
But in 2025, many of these signals were weak or simply vanished. The winds, a major driving force behind the ocean’s churning, failed to line up with the pattern researchers had come to expect. As a result, chlorophyll concentrations in the Panama Gulf were desperately low.
For the first time in living memory, Panama’s Pacific waters skipped their annual cold-water recharge.
Wind may be the key to understanding this unusual situation. The researchers’ paper notes that the lack of upwelling in 2025 “appears linked” to weak, shorter, and less frequent winds in this corner of the Pacific.
They suspect this might have something to do with the La Niña that emerged in the tropical Pacific around December 2024, especially in regard to its effect on the Intertropical Convergence Zone, the region near the equator where the trade winds of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres meet. However, the study admits that the “mechanisms remain unclear.”
Regardless of the cause, the impact on life could be severe. The annual upwelling in the Gulf of Panama is part of the reason why the shores in this part of the world remain relatively cool in the “summer vacation” months. The relatively chilled waters also provide refuge for the region’s coral reefs, which can become stressed with intense heat.
Perhaps most pressingly, the missing upwelling could ripple through Panama’s fish stocks. Normally, the seasonal surge of cold water delivers a fresh supply of nutrients that fuels blooms of phytoplankton, the microscopic plants that support much of the ocean food web. And for many coastal communities, those fish are a vital source of food and income. Without that nutrient recharge, the whole system risks running on empty.
Looking ahead, oceanographers and marine biologists are keen to see whether 2025 was a one-off or the worrying start of something new.
“Whether the 2025 event signals the first of future failed upwellings warrants investigation through enhanced monitoring, predictive modelling, and targeted research on the interactions between oceanography, ecology, and human resource dependence in tropical upwelling systems,” the study concludes.
The study is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Source Link: For The First Time, A Vital Oceanic Upwelling Of Nutrient-Rich Water Failed To Emerge In 2025