Living things have been known to glow thanks to a nifty trick called bioluminescence, but it’s something we more typically associate with animals of the deep sea than those stomping around surface-side. It may surprise you, then, to learn that bioluminescence has been detected in humans. That’s right, we glow in the dark – it’s just really, really, really faint.
That was the discovery made by researchers in a 2009 study who used incredibly sensitive cameras to effectively watch naked people sleep. Bit creepy, sure, but it also shone a light on the light that we unknowingly emit.
“The human body literally glimmers,” wrote the study authors, and as for why we can’t see it? “The intensity of the light emitted by the body is 1000 times lower than the sensitivity of our naked eyes.”
The glimmering was observed in five males in their 20s who were subjected to normal light-dark conditions and invited to periodically snooze in front of a cryogenic charge-coupled device (CCD) camera that could detect light at the level of a single photon. The researchers note that the camera had to be operated at –120 °C (-184 °F), but fortunately the participants weren’t subjected to the same.
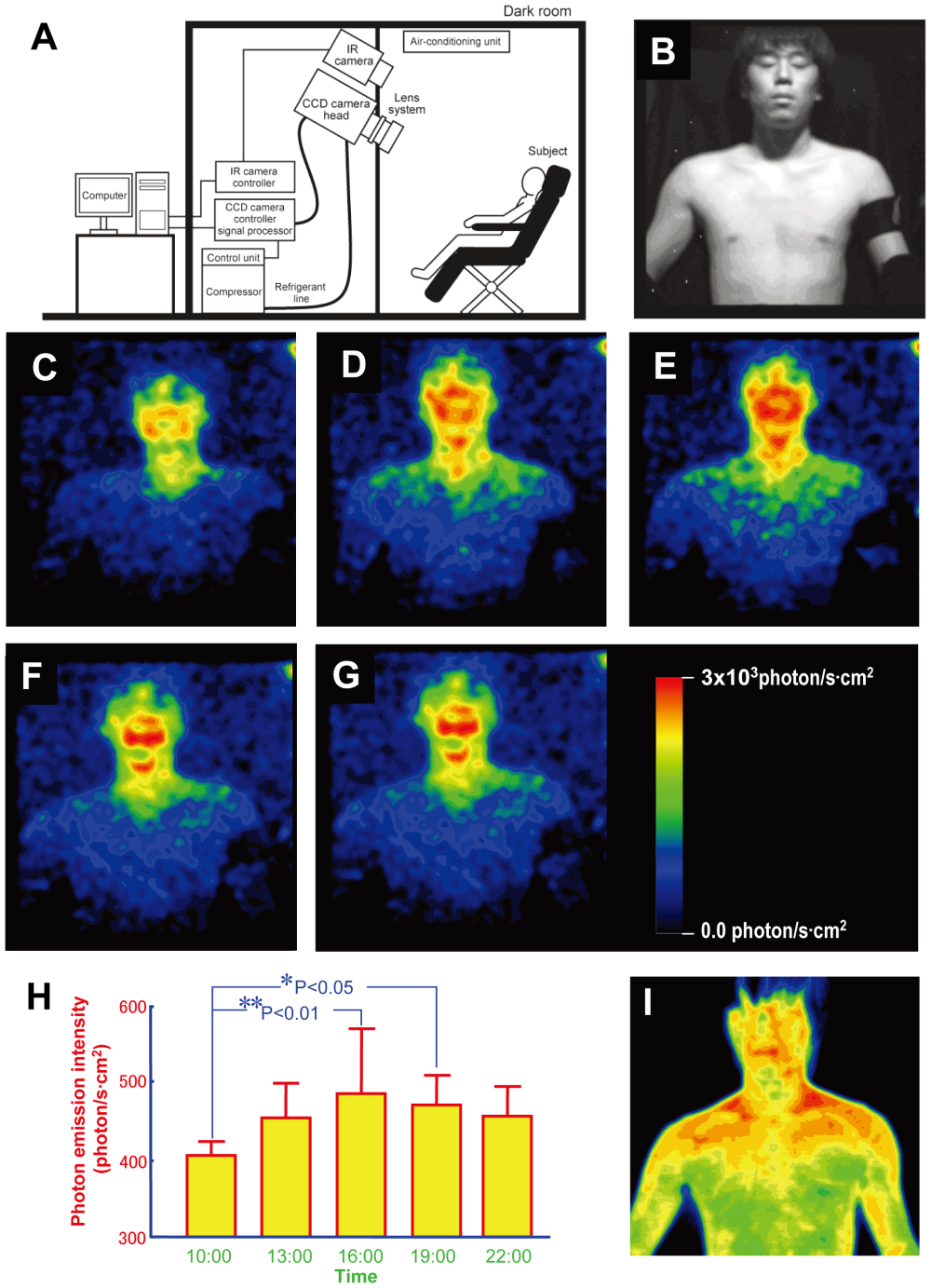
A. The experimental setup. B–F. Images of ultraweak photon emission from human body, including the subject under light illumination. G Calibration bar for estimated radiation intensity on skin’s surface. H. Daily rhythm of photon emission from face and body from 5 volunteers. I. A typical thermographic image of the subject from B-G.
They were, however, routinely sampled for saliva to measure cortisol levels, and had their surface and oral temperature checked before and after photon measurements were taken. Cortisol is a biomarker of endogenous circadian rhythms, which the researchers wanted to have tracked so that they could compare it against any changes observed on the camera.
As it happens, it seems the way we glow does change throughout the day, with our faces glowing the most. As for what is orchestrating that change, it likely all comes down to our circadian rhythms.
Chronobiology is a branch of science that studies cyclical physiological phenomena, and it’s established that the circadian clock is the main regulator of metabolism. We see it in the way we burn up glucose and consume oxygen, both of which – the researchers say – show robust rhythms in the main mammalian circadian center.
That “powerhouse” of the cell, good old mitochondria, releases tiny amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a byproduct while it’s producing the energy needed to keep us alive. These ROS react with molecules including proteins, lipids, and fluorophores, whose excited states emit biophotons, and this is how “the human body glitters to the rhythm of the circadian clock.”
Well, aren’t we fancy.
Bioluminescence relies on enzymatic activity to glow, but there’s also another way that living things can glow and we’re increasingly finding it in more and more species.
Source Link: Humans Glow In The Dark, It’s Just Too Weak For Our Eyes To See