Scientists have grown “mini-antlers” on mice by inserting deer genes into the mouse genome, according to a new paper. The results suggest that mammals that have lost the ability to regenerate organs may still contain some regenerative genes, and that it may be possible to harness the rapid growth of antlers in other applications.
Growing at 2.75 centimeters (around 1 inch) per day, antlers are one of the fastest regenerating tissues in the animal kingdom and offer a perfect look at how mammals can regenerate cells on a regular basis. Antlers are especially interesting because mammals in general have lost the ability to regenerate organs and most other tissues, so a large appendage that regularly regrows offers unparalleled insight into how regenerative medicine for bones could work.
In the pursuit of regenerative medicines, Chinese researcher Toa Qin and colleagues took a deep dive into the mechanics behind the antlers of Sika deer, which regrow every year before they are shed. In doing so, they created a regenerative “atlas” of Sika deer antlers, isolating multiple single cells and genes that are critical in the development of the antler tissue.
Ten days before the antlers were shed, the researchers identified one type of stem cell that was highly active in the regeneration, and these remained with the antlers a short time after shedding. However, by day five post-shedding, a new subtype of stem cells had emerged.
After identifying multiple stages of growth, the team took the stem cells with the most regrowth potential (which proved to be from shed antlers around five days old) and cultured them in a Petri dish before implanting them into the head of mice.
After 45 days, the mice had developed clearly identifiable mini-antlers, owing to the stem cells differentiating into osteochondral tissue, which is integral to bone fracture repair. The antlers had elongated rapidly, displaying the genetic mechanisms that result in their development to the researchers and giving insights into how they could be utilized in human bone medicine.
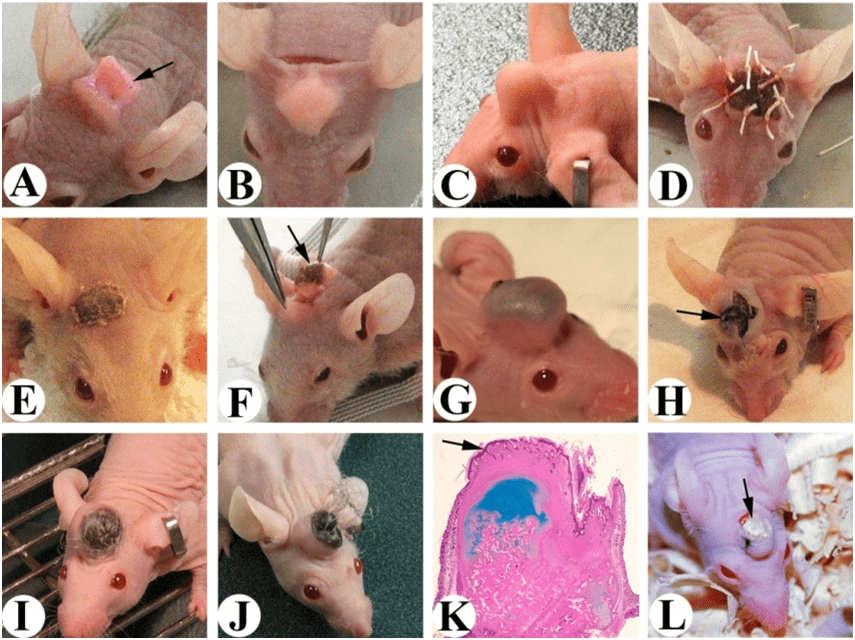
The mice with the “mini-antlers” growing on their heads, from a previous report by one of the study authors. Image credit: Li, Journal of Regenerative Biology and Medicine (2020)
Such a treatment could raise ethical concerns about the cross-species implantation of cells, as well as the significant safety trials that would be required before it could be submitted for approval. However, if the mechanisms underlying regeneration can be uncovered, it is possible that analogous genes could be found within mammals.
While the results can’t quite be translated straight into repairing broken legs, it gives a brand-new look into exactly how mammals can regenerate tissue, both by mechanisms within our genomes and with a little help from antler stem cells.
The study is published in Science.
Source Link: "Mini Antlers" Grown On Mice Heads After Scientists Implant Deer Cells