Eclipse fever is not just for those looking forward to spectacular sights next week. NASA will launch three sounding rockets to see how the temporary blocking of sunlight affects the upper atmosphere as part of APEP (Atmospheric Perturbations around Eclipse Path, but also the name of the Egyptian Sun God’s nemesis).
Starting 90 kilometers (55 miles) up, the ionosphere is well above the highest clouds, so it‘s usually exposed to sunlight throughout the day. Eclipses are the one exception, and provide an opportunity to study it in ways dusk does not. Most eclipses lack suitable launch sites, at least in the path of totality – but the eclipse of April 8 passes conveniently close to some major American sites.
The APEP team, led by Professor Aroh Barjatya of Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Florida, has put new instruments on three sounding rockets they launched from White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico during the 2023 annular eclipse. These will explore the ionosphere to a height of 420 kilometers (260 miles) during the eclipse’s peak, as well as 45 minutes before and after.
The ionosphere is “an electrified region that reflects and refracts radio signals, and also impacts satellite communications as the signals pass through,” Barjatya said in a statement. “Understanding the ionosphere and developing models to help us predict disturbances is crucial to making sure our increasingly communication-dependent world operates smoothly.”
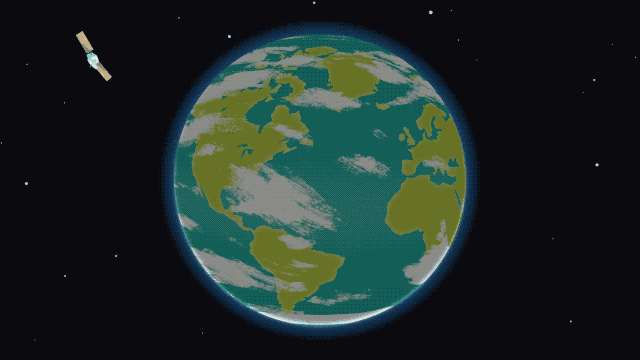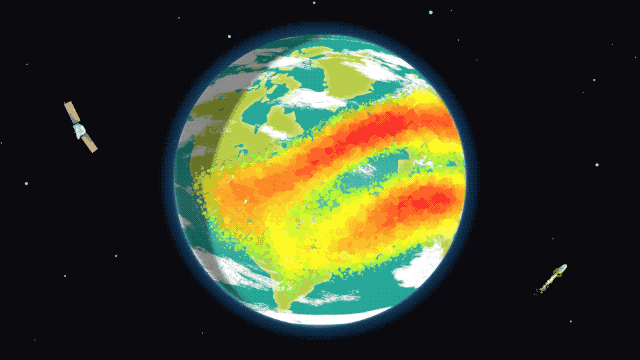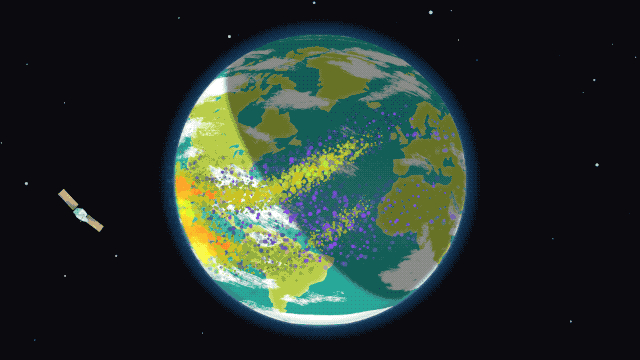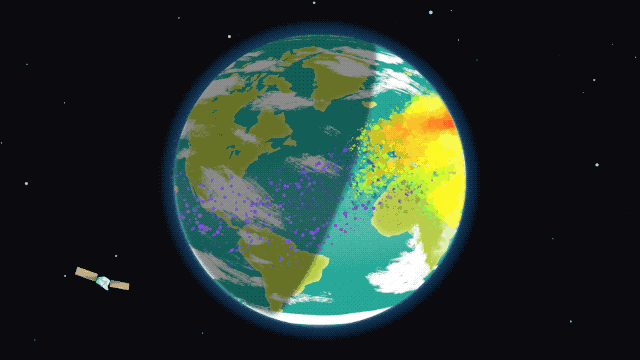
The ionosphere during an ordinary day/night cycle. Red and yellow represent high-density ionized particles, seen during the day. The purple dots represent neutral, relaxed particles at night
Image Credit: NASA/Krystofer Kim
Sunlight, of course, affects all parts of the atmosphere – but the ionosphere is a creation of that light. High-energy photons separate atoms into electrons and positively charged ions. At night they recombine, so the ionosphere declines. Weather conditions lower down in the atmosphere also play a part, creating a more complicated picture.
Satellites have revealed an even bigger impact from eclipses, but those suitably equipped with instruments are seldom in the right place at the right time for observations. The rockets, on the other hand, can be timed at scientists’ will. The path of totality passes to the west of the Wallops Island, Virginia, launch site. However, the APEP team consider it close enough to get the data they need.
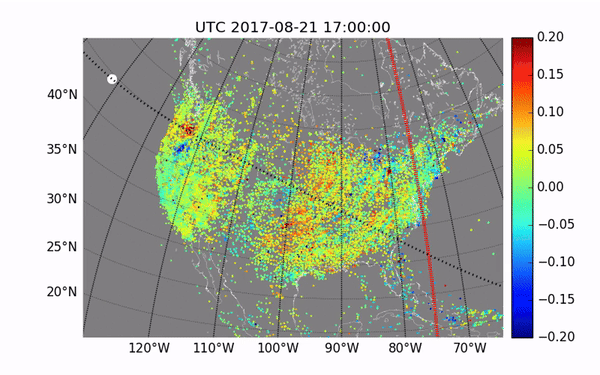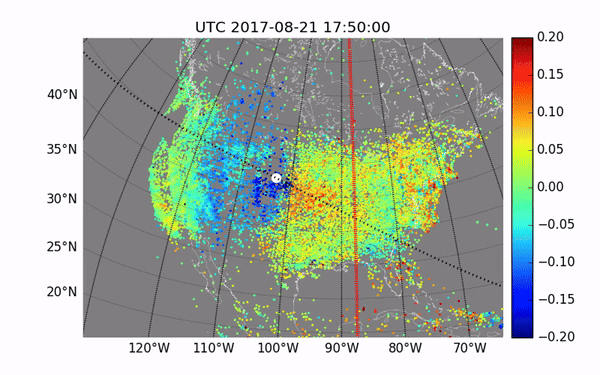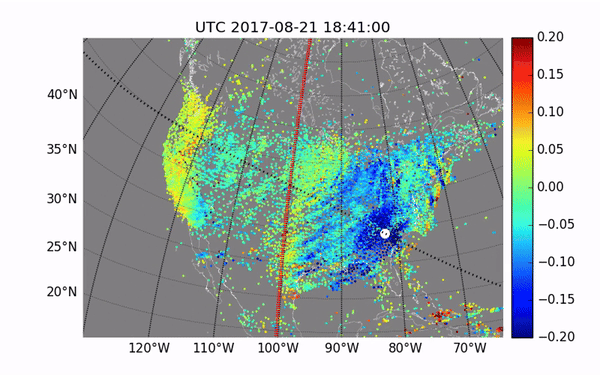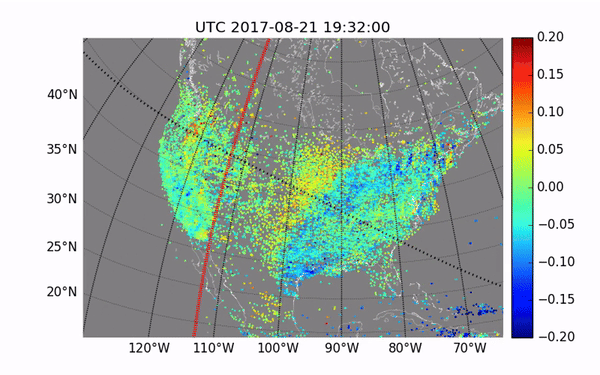
The waves created by ionized particles during the 2017 total solar eclipse
Image Credit: MIT Haystack Observatory/Shun-rong Zhang
Observations of previous events reveal atmospheric waves that affect the entire path of the eclipse, as well as more localized disturbances known as perturbations, which can interfere with radio signals. The changes can be seen in variations in both temperature and plasma density.
The rockets will compare the density of charged and neutral particles at the three points during the eclipse. “Each rocket will eject four secondary instruments the size of a two-liter soda bottle that also measure the same data points, so it’s similar to results from fifteen rockets, while only launching three,” Barjatya said. The work will be further supported using high-altitude balloons, ground-based radar, and some satellite observations.
The rockets’ launch during the 2023 annular eclipse is shown above. A steep drop in plasma density on that occasion was reported at the American Geophysical Union conference.
“We saw the perturbations capable of affecting radio communications in the second and third rockets, but not during the first rocket that was before peak local eclipse,” said Barjatya. “We are super excited to relaunch them during the total eclipse, to see if the perturbations start at the same altitude and if their magnitude and scale remain the same.”
Source Link: NASA To Send Rockets To Study The Eclipse’s Effect On The Ionosphere