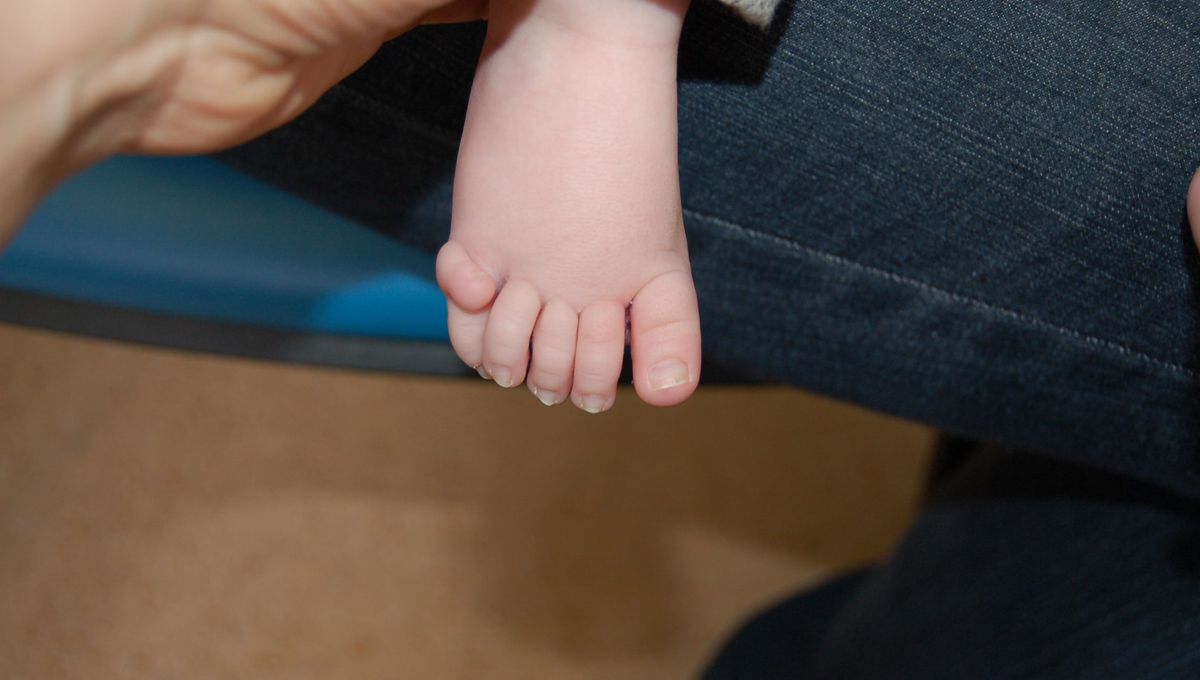
By comparing the DNA of individuals born with a range of birth defects, including extra fingers and toes, researchers have identified a new rare disorder and with it, opened up an avenue towards improved diagnosis and treatment.
The findings were described in a study that examined three children sharing a rare combination of traits: polydactyly, more often known as extra fingers and/or toes; a larger than average head circumference; and delayed development of their eyes.
These features suggested the young patients may share a disorder, although what had caused it was unknown. Researchers set to analyzing their DNA, which revealed all three had the same mutation in a gene called MAX. It’s a gene that encodes a protein known as a transcription factor, a molecule that’s involved in copying DNA into RNA.
Identifying this mutation means that it could be easier to diagnose others with the disorder in future, study co-lead, Dr James Poulter, explained in a statement. “Other patients with a similar combination of features can be tested to see if they have the same variant we have identified in our study.”
Poulter added: “Currently there are no treatments for these patients. This means that our research into rare conditions is not only important to help us understand them better, but also to identify potential ways to treat them.”
On that front, the study succeeded. The team identified a molecule that could be used to prevent worsening of the disorder and treat its neurological symptoms, though this would require extensive research before becoming an approved treatment. It helps that it’s already in clinical trials for another disorder, “meaning we could fast track this for these patients if our research finds the drug reverses some of the effects of the mutation,” according to Poulter.
Although a treatment may still be a while off, the authors plan to further investigate the MAX mutation and are keen to highlight the importance of this kind of research, which often gives patients and their families long-awaited answers. For example, the study used data from the Deciphering Developmental Disorders study, a UK-based project that’s led to a multitude of diagnoses for patients with rare diseases.
“These are often under-represented conditions that have a huge impact on patients and their families. These families go through a long and complex diagnostic odyssey. The time from their first doctor’s visit as babies to getting a diagnosis can take more than 10 years,” Poulter explained.
“It is important that these patients and their families discover the cause of their condition – and if they can access a therapy based on their genetic diagnosis, that could be life changing.”
The study is published in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
Source Link: Rare Disorder Causing Extra Fingers And Toes Identified From DNA Differences