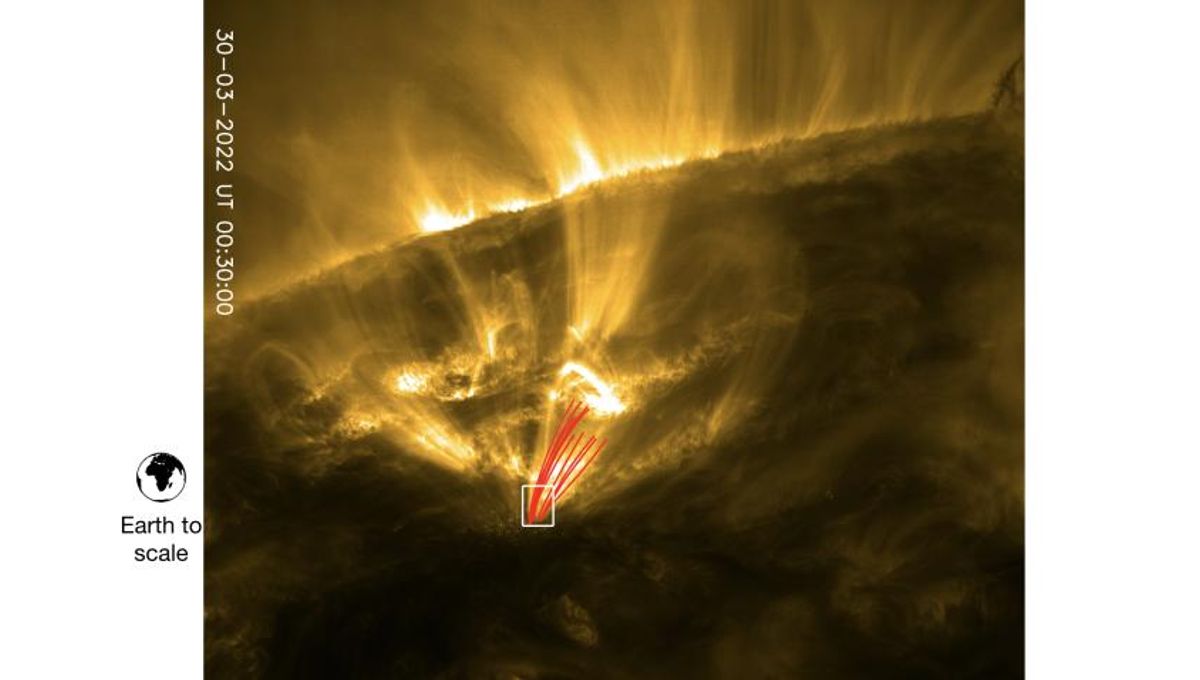
An international team of astronomers has discovered a never-seen-before feature in the solar corona: “shooting stars” falling down on the Sun. Using the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter (SolO), they discovered that the phenomenon of coronal rain was hiding these meteor-like fireballs, which can get as big as 250 kilometers (155 miles) wide.
Don’t let the name fool you, coronal rain is not made of water. The solar corona, the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere, has a temperature of millions of degrees and is made of plasma. Occasionally, the temperature drops in these regions and plasma clumps up. The temperature of these clumps is still in the tens to hundreds of thousands of degrees, though. They are not cold per se, just colder and denser than the surrounding areas.
The huge gravitational force that the Sun exerts pulls them towards it at an incredible 100 kilometers (61 miles) per second, so there is a fireball effect as they plunge toward the Sun. Given how thin the solar corona is, the team thinks most of these fireballs make it to the surface intact. SolO has even observed such impacts on the solar surface, impacts that released shockwaves and an upsurge of material.
“It’s kind of a shooting star on our star,” lead author Dr Patrick Antolin from Northumbria University told IFLScience. “We also observed the effects of when these clumps fell and impacted the surface of the Sun. They produce a large surge of gas that propagate in the corona reheating it.”
The observations come from SolO’s first perihelion, the closest point to the Sun in an orbit. In spring 2022, SolO was at about one-third of the distance between Earth and the Sun. From that vantage point, the spacecraft was able to see the solar corona in unparalleled detail, which made the discovery possible.
“With one of the instruments, we can see that this coronal rain is a bit everywhere in this active region of the Sun,” Dr Antolin continued.
Despite some similarities, these fireballs are not like the ones we see on Earth. Meteors are created by small rocky or icy materials (some as small as a dust grain) that enter our atmosphere at high-speed. The friction burns them up creating bright long trails. The fireballs of the Sun are compressed by magnetic fields. The plasma clumps actually follow the magnetic fields like they were a funnel all the way to the surface. Without a tail, it is more difficult to identify these clumps.
“In the solar corona, the material cannot go back, cannot be stripped and form a tail,” Dr Antolin explained to IFLScience. The magnetic field is too strong and creates a funneling effect. It all stays ahead, and this is also why it is so difficult to observe. It is very bright but only underneath.”
The study was presented at the National Astronomy Meeting 2023 and will be published in a special issue of Astronomy & Astrophysics dedicated to SolO’s first close perihelion to the Sun.
Source Link: "Shooting Stars" Discovered In The Sun’s Corona For First Time