Brains, eyes, and digestive organs. Those were just some of the soft tissue surprises waiting for researchers processing 462-million-year-old specimens retrieved from Castle Bank Quarry in Wales, UK. The Castle Bank Community, as the collection of ancient marine oddities is known, demonstrates remarkable diversity as well as preservation, contributing more than 170 new species to science with the help of crowdfunding.
Exceptional specimens such as these are sometimes called Burgess Shale-types after a location in Canada where fossils were found with soft tissues preserved, extending our understanding of the evolution of animal groups. Typically, they’re limited to the Cambrian period that stretched between 541 and 485 million years ago, but on occasion, science is treated to an extra old glut of gorgeous fossils.
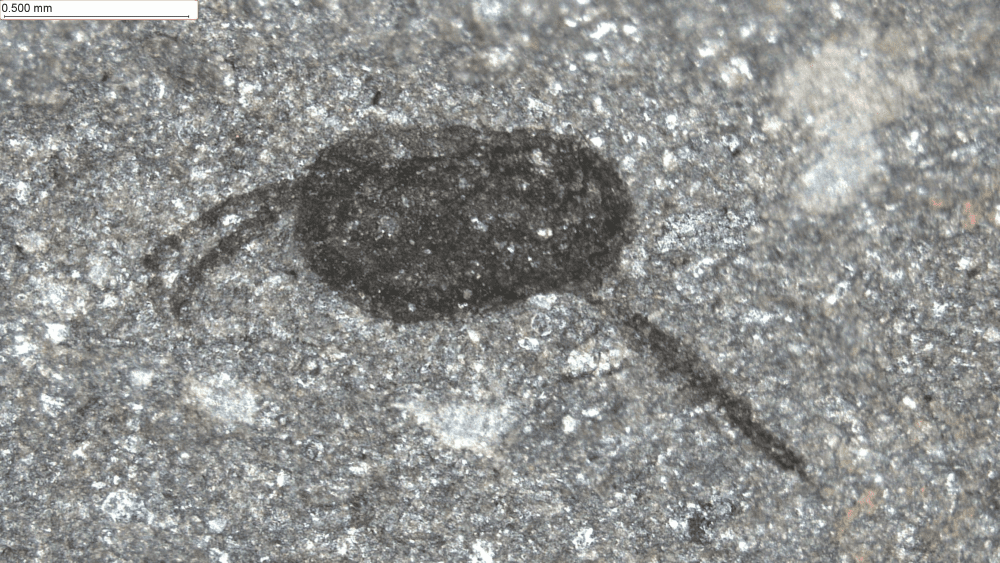

A new species of tiny bivalved arthropod with long grasping appendages (left). Image credit: Joe Botting
That could be said of the Castle Bank Community which dates back to 462 million years ago, landing them in the Middle Ordovician epoch. They are mostly small in size, sitting between 1 to 5 millimeters in total body length (0.04 to 0.2 inches).
Organisms among the Castle Bank Community include worms, starfish, sponges, crustaceans, and arthropods, making for quite the colorful cast of Ordovician marine beasties. Such a roster gives scientists a magnificent snapshot of the lives of some of the earliest animal-dominated communities, allowing them to track ecological development across time.
As well as being incredibly diverse, the Castle Bank Community was also incredibly well preserved. Soft tissues found among the fossils included eyes, optic nerves, brains, and digestive tissues. They also demonstrated unexpectedly small body sizes, which the researchers hypothesize could’ve been an adaptive response to their changing ecology.
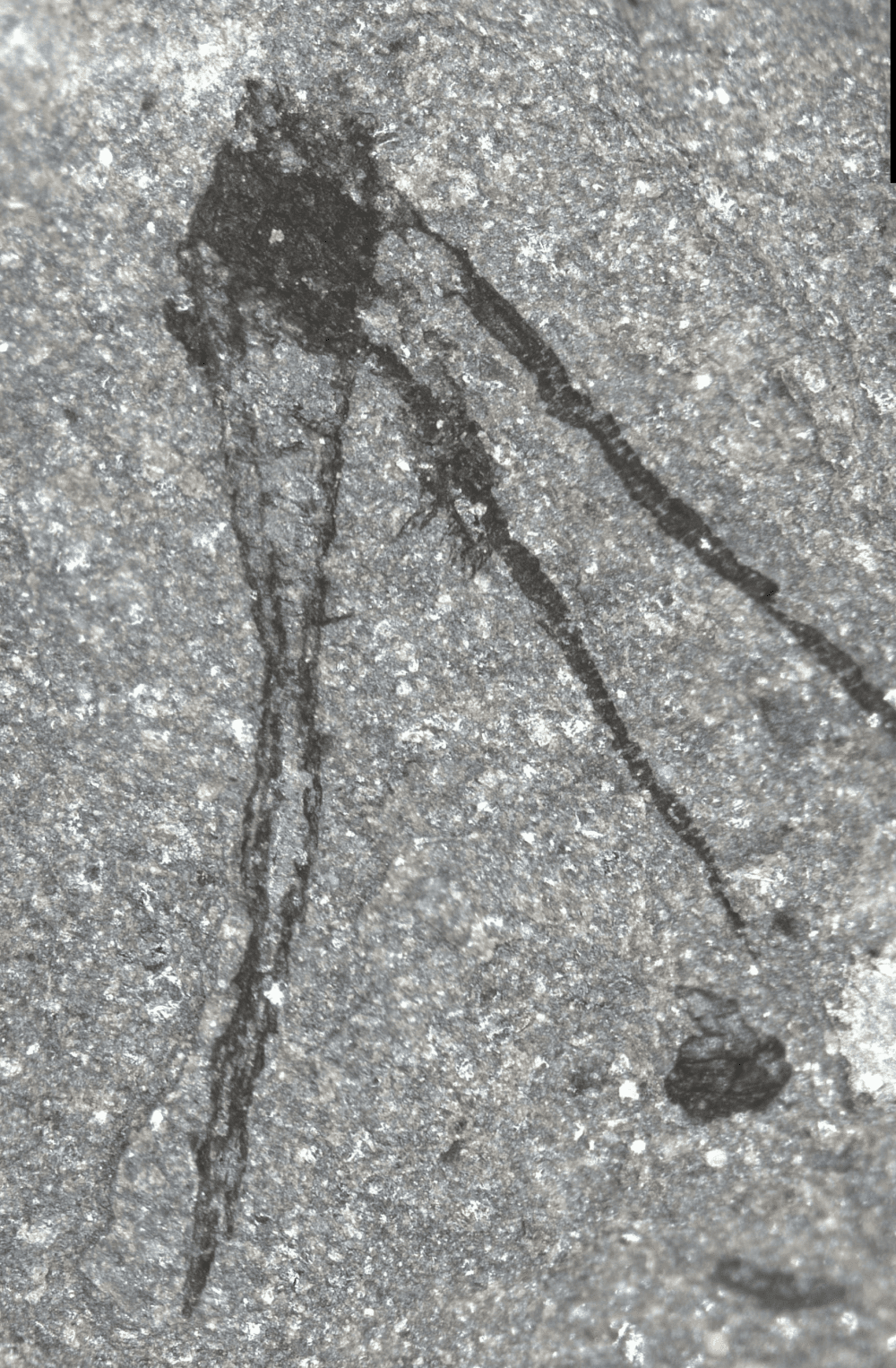
A strange, tube-dwelling animal with two long tentacles and a delicate lobe of soft tissue. Image credit: Joe Botting
“Many of the exceptionally preserved fossils (for example, tube-dwelling organisms and algae) were small and sessile but do not have holdfasts or attachment preserved, suggesting that they were forcibly removed from a hard substrate before burial,” they explained. “The small size of many of the Castle Bank species may therefore reflect an expected phase of ecological evolution between the Cambrian and modern faunas, revealed here in a specific community that was possibly associated with undersea rock exposures.”
There are several possible drivers that could’ve made small size and mobility beneficial traits in the Middle Ordovician epoch, including changes in predation strategy or the distribution of nutrients during what the authors term a “phytoplankton revolution”. Whatever the cause, the Castle Bank Community is an example of how miniaturization was occurring with specific ecosystems at this time, though questions remain as to how widespread it was.
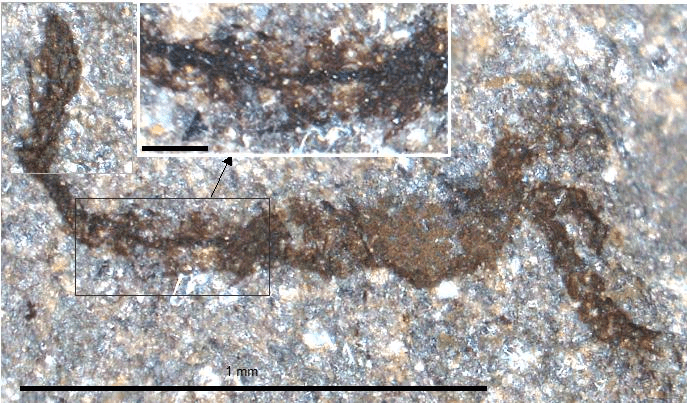

A new species of arthropod with visible gut (dark line down the body). Image credit: Joe Botting
The fossil bonanza in Wales was made possible thanks to a crowdfunding project that raised money to fund the microscopy equipment needed for gleaning insights from such miniature specimens. With more than 170 species already under the researchers’ belts, it’s hoped the project’s efforts will yield even more in future, shining light on a murky period in the evolution of early animals.
The study is published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
Source Link: Incredibly Preserved Fossils Show How Weird The Sea Was 462 Million Years Ago