Astronomers have produced the sharpest view yet of the R136 star cluster and its most famous inhabitant R136a1, the heaviest star in the cosmos as far as humans know. This incredibly massive object has now been seen with such clarity that the team was able to refine the mass estimates, something that has profound consequences not just for our understanding of stars but for our understanding of the universe as a whole.
The study, accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal, reviews the mass estimate of this object – which was previously thought to be up to 320 times the mass of the Sun – to a range between 170 and 230 solar masses. While still a record-breaking object, these observations suggest that maybe extremely massive stars are much rarer than anticipated.
While we urge caution when interpreting our results, our observations indicate that the most massive stars may not be as massive as once thought.
Dr Venu Kalari
“Our results show us that the most massive star we currently know is not as massive as we had previously thought,” lead author Dr Venu Kalari said in a statement. “This suggests that the upper limit on stellar masses may also be smaller than previously thought.”
While regular stars like the Sun live for billions of years, massive stars burn brightly and die young in supernovae. A very specific kind of supernova is expected to happen for stars with a mass of more than 150 times the Sun: They would end up in a pair-instability supernova.
These events are so catastrophic that they do not leave behind a black hole or neutron star. The entire star is destroyed and its layers are turned into elements heavier than hydrogen and helium and spread through the universe. We are here today because massive stars in the past did exactly that. We are made of those elements. If the mass of other stars has been overestimated, pair-instability supernovae might be rarer than thought, which has implications for our understanding of how the universe became what it is today.
The observations were conducted at the Gemini South telescope of the International Gemini Observatory. They used the Zorro instrument – which is Spanish for fox – and a new technique to see the star cluster, which is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a neighboring galaxy of the Milky Way. Zorro allowed to see the individual stars in the cluster and so reduce the uncertainty on their mass.
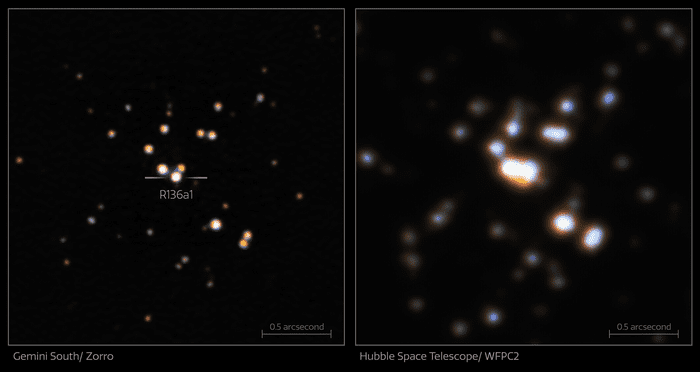
Comparison between the Zorro and Hubble Image. Image Credit: International Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA Acknowledgment: Image processing: T.A. Rector (University of Alaska Anchorage/NSF’s NOIRLab), M. Zamani (NSF’s NOIRLab) & D. de Martin (NSF’s NOIRLab); NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope
“We began this work as an exploratory observation to see how well Zorro could observe this type of object,” explained Kalari. “While we urge caution when interpreting our results, our observations indicate that the most massive stars may not be as massive as once thought.”
The technique used is called speckle imaging and, together with adaptive optics, it can counteract the blurring effect of Earth’s atmosphere. The approach works by taking many thousands of short-exposure observations that are then processed to obtain resolution comparable to, and in this case exceeding, the observation of space telescopes.
“This result shows that given the right conditions an 8.1-meter [26.6-foot] telescope pushed to its limits can rival not only the Hubble Space Telescope when it comes to angular resolution, but also the James Webb Space Telescope,” commented Ricardo Salinas, a co-author of this paper and the instrument scientist for Zorro. “This observation pushes the boundary of what is considered possible using speckle imaging.”
Source Link: This Is The Best Ever Image Of The Heaviest Star In The Known Universe