There’s a good chance you’ve never heard of it, let alone seen it, but this may be one of the most ubiquitous animals on the planet.
Alicella gigantea is basically a big, pale shrimp-like creature that lives in the deepest depths of Earth’s oceans. It has the title of being the world’s largest amphipod, an order of crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies, with some individuals reaching up to 34 centimeters (13 inches) in length.
First described in 1899, very little is known about this “supergiant amphipod”, but they’re known to inhabit depths of 3,890 to 8,931 meters (12,762 to 29,302 feet).
But don’t be misled by their uncharismatic blurb and elusive reputation – this organism is incredibly successful.
In a new study, scientists at the University of Western Australia in Perth compiled nearly 200 records of A. gigantea from 75 locations worldwide across the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, and concluded that it may occupy around 59 percent of the world’s oceans.
“This finding confirms that the supergiant amphipod is far from ‘rare’ but instead represents a single, globally distributed species with an extraordinary and expansive range across the deep sea,” the study authors write.
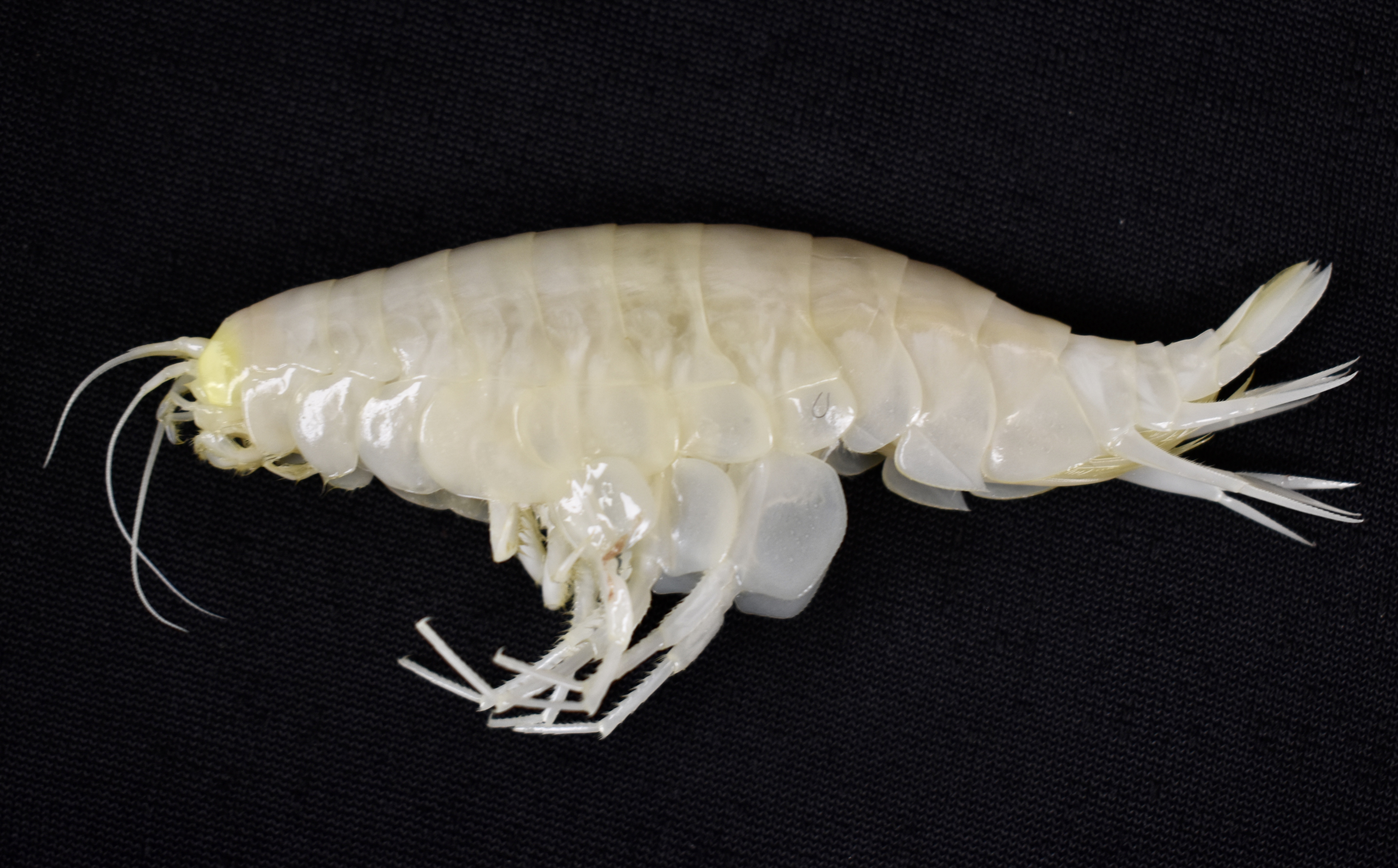
An Alicella gigantea specimen collected from Japan Trench in 2022.
Take a moment to think about the vastness of the world’s seas. Around 71 percent of Earth’s surface is covered by sea, meaning the seabed is one of the largest ecosystems on Earth.
It might not be very pretty, but A. gigantea is beautifully adapted to life in the hadal zone, Earth’s deepest, darkest, and most extreme marine environment. A 2021 study looked at the DNA of this species and found they have a unique collection of genes linked to energy conservation, starvation resistance, and pressure-tolerant meiosis that appear to play central roles in their survival strategy.
Weirdly, their large size might also be part of this ability to survive and thrive in the deep sea. Unique genetic markers in this amphipod – especially a standout gene called aPKC, also linked to gigantism in mammals like the capybara – suggest that its massive size is not just an accident of evolution, but a finely tuned adaptation. Enhanced growth regulation and efficient energy use might allow A. gigantea to store more resources and survive longer without food, which gives it an edge in the abyss where food is scarce.
The study is published in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
Source Link: This Strange, Supergiant Amphipod Inhabits Up To 59 Percent Of The World's Seabed