Most of the black holes we know of are in two categories. They are either supermassive, millions or billions of times the mass of the Sun, or stellar-sized, from a few times to a few tens of times our little star. There is an in-between category known as intermediate mass black holes (IMBHs) that weigh from 100 or so to a few hundreds of thousands of times the mass of the Sun. Only a few of these IMBHs are known, and astronomers have now caught another one.
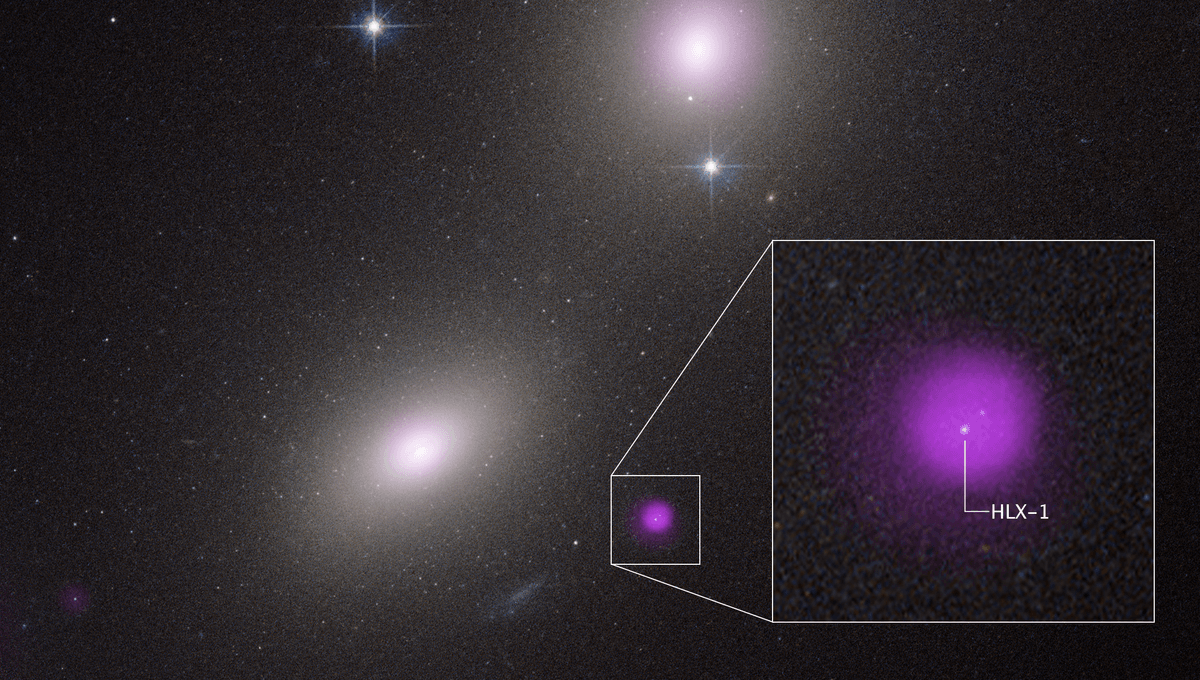
This one, NGC 6099 HLX-1, was first seen in 2009 when it suddenly became incredibly bright in X-rays. First NASA’s Chandra and then the European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton tracked how this object changed, peaking in 2012. The observatories revealed that it is 40,000 light-years from the center of its galaxy, NGC 6099, located about 450 million light-years away in the constellation Hercules.
Supermassive black holes, sitting at the core of galaxies, are known to be active and emit a lot of X-rays. Finding one way off-center suggested the possibility of an IMBH. The X-ray data indicate that the object reached 3 million kelvins, consistent with a black hole ripping apart a star, something called a tidal disruption event.
“X-ray sources with such extreme luminosity are rare outside galaxy nuclei and can serve as a key probe for identifying elusive IMBHs. They represent a crucial missing link in black hole evolution between stellar mass and supermassive black holes,” lead author Yi-Chi Chang of the National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, said in a statement.
Hubble data revealed that NGC 6099 HLX-1 is surrounded by a cluster of stars, so there are plenty of opportunities for snacking. The peak was in 2012, and it has been declining all the way to the last observations in 2023, but optical and X-ray views do not overlap exactly. The disruption of the star might have created a plasma disk of variable luminosity, or the disk might flicker due to the IMBH eating some of the gas over time.
“If the IMBH is eating a star, how long does it take to swallow the star’s gas? In 2009, HLX-1 was fairly bright. Then in 2012, it was about 100 times brighter. And then it went down again,” explained study co-author Roberto Soria of the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF). “So now we need to wait and see if it’s flaring multiple times, or there was a beginning, there was [a] peak, and now it’s just going to go down all the way until it disappears.”
Understanding IMBHs could be crucial to understanding how supermassive black holes came to be. The team hopes to find more of these objects as they do something energetic, like ripping a star apart.
“So if we are lucky, we’re going to find more free-floating black holes suddenly becoming X-ray bright because of a tidal disruption event. If we can do a statistical study, this will tell us how many of these IMBHs there are, how often they disrupt a star, how bigger galaxies have grown by assembling smaller galaxies,” said Soria.
The study is published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Source Link: Extremely Rare Black Hole Type Caught Snacking On A Star 450 Million Light-Years Away