A few years ago, strange black stains began to appear on a collection of Leonardo da Vinci’s most famous drawings and writings: The Codex Atlanticus. The codex, housed since 1997 in a controlled micro-climate at Biblioteca Ambrosiana, Milan, began showing signs of blackening. Investigation showed that these darkened patches were on some 210 pages of the codex.
The stains were, of course, concerning to the curators, who worried that the biggest collection of da Vinci’s drawings and writings could be lost to whatever the patches were. The patches were studied, but it wasn’t altogether clear what was causing them.
Previous studies ruled out the stains being caused by microbiological deterioration. However, new research which examined the pages using hyperspectral photoluminescence imaging and UV fluorescence imaging found starch and vinyl glue in the heavily stained areas of the codex, at the edges of the pages where they are bound.
“A mixture of PVAc and starch glues was detected in the area closer to the folio, which is the area that appears darkened,” the team wrote in their paper. “It remains to be determined whether degradation reactions of this synthetic glue (together with paper hydrolysis) might have played a role in promoting the blackening phenomenon.”
The team also found round inorganic nano-particles made up of mercury and sulfur within cavities on the passepartout paper separating the pages of the codex, which they identified as metacinnabar: mercury sulfide in “an unusual black crystalline phase”.
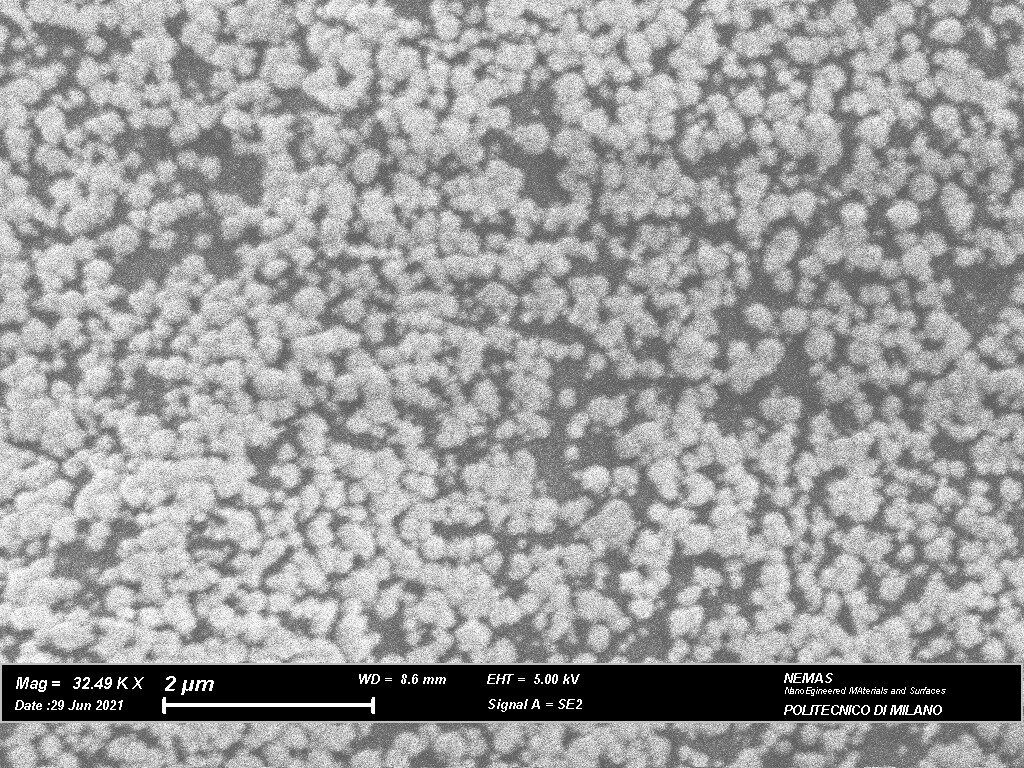
Mercury and sulphur on the Codex. Image credit: Politecnico di Milano
“In-depth studies on paper preservation methods have allowed us to formulate some hypotheses on the formation of metacinnabar,” the team said in a press release. The team believes the deposits were the result of restoration on the codex which took place at the Abbey of Grottaferrata between 1962 and 1972, when the codex pages were separated with passepartout.
“The presence of mercury could be associated with the addition of an anti-vegetative salt in the glue mixture used in Grottaferrata’s restoration techniques, which could have been applied only in certain areas of the passepartout paper, precisely where it holds Leonardo’s folio, to ensure adhesion and prevent microbiological infestations on the Codex,” they added.
“The presence of sulfur, on the other hand, has been linked to air pollution (in Milan in the 1970s, levels of sulfur dioxide SO2 were very high) or to the additives used in the glue, which over time would have led to a reaction with mercury salts and the formation of metacinnabar particles, responsible for the black stains.”
The study was published in Nature.
Source Link: The Black Stains On Leonardo Da Vinci's Codex Atlanticus Explained