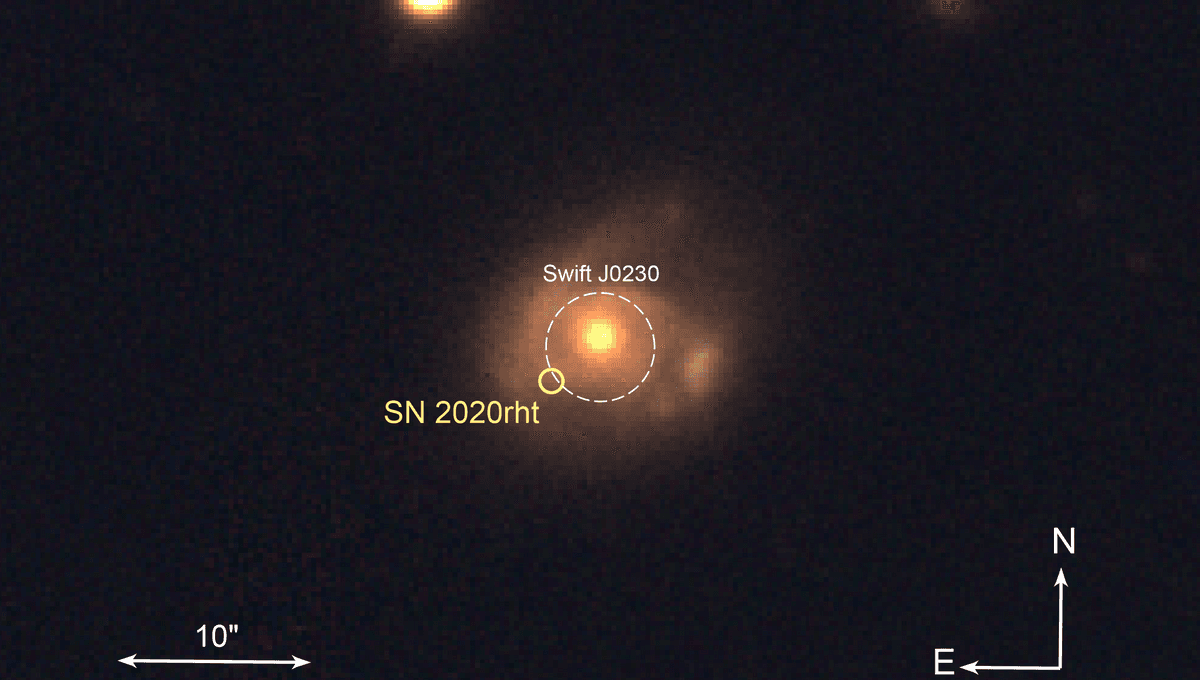
Astronomers have observed for the first time an intermediate-mass black hole tearing chunks off a star as it repeatedly passes by it. These mouthfuls are roughly equivalent to the mass of three Earths every 25 days or so.
The star in question is roughly the mass of our Sun, but the black hole is the one with a surprising mass. Despite sitting at the center of its galaxy, the black hole in question is not supermassive like it is expected to be. They estimate that the black hole is around 10,000 to 100,000 times the mass of our Sun, in the elusive class of intermediate-mass black holes.
It is much heavier than the ones you get from a supernova explosion, roughly the mass of a star, and those supermassive ones you usually find at the galactic core. Sagittarius A* at the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way, is over 4 million times the mass of the Sun.
“This is the first time we’ve seen a star like our Sun being repeatedly shredded and consumed by a low mass black hole,” lead author Dr Phil Evans of the University of Leicester School of Physics and Astronomy said in a statement sent to IFLScience. “So-called ‘repeated, partial tidal disruption’ events are themselves quite a new discovery and seem to fall into two types: those that outburst every few hours, and those that outburst every year or so. This new system falls right into the gap between these, and when you run the numbers, you find the types of objects involved fall nicely into place too.”
The event is nicknamed Swift J0230, from the observatory Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory. As the star passes close to the black hole, some of its material is pulled apart. The material spirals toward the black hole, where the intense pull of gravity heats it up to millions of degrees.
The hot plasma emits X-rays that can be spotted by the Swift observatory. The object, located 500 million light-years from Earth, brightens for 7 to 10 days during its meal before dimming waiting for the star to pass by again.
“In most of the systems we’ve seen in the past the star is completely destroyed. Swift J0230 is an exciting addition to the class of partially-disrupted stars as it shows us that the two classes of these objects already found are really connected, with our new system giving us the missing link” added co-author Dr Rob Eyles-Ferris, who works with Dr Evans on the Swift satellite and recently completed his PhD at Leicester.
The work was possible thanks to a new setup that allows the satellite to follow up on transient X-ray emissions that appear where no X-rays were there before. Events such as Switch J0230 would have not been easy to find before this approach. And many more await discovery.
“Given that we found Swift J0230 within a few months of enabling our new transient-hunting tool, we expect that there are a lot more objects like this out there, waiting to be uncovered,” Dr Kim Page from the University of Leicester, who worked on the data analysis for the study, explained.
The research is published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Source Link: Three Earth's Worth Of Star Stuff Is The Regular Meal Of Ravenous Black Hole