Does it matter which arm you get your shots in? The short answer is yes, and not just because you probably want to avoid post-injection pain on your dominant side. Getting a vaccine booster in the same arm as the original shot can generate a better immune response, and now scientists are figuring out why.
Most vaccines contain an inactivated or attenuated (weakened) form of the disease they’re trying to protect you against – the antigen. The MMR, for example, contains live but significantly weakened measles, mumps, and rubella viruses. Instead of making you sick, they teach your immune system to be ready for when you encounter the real thing out in the wild.
When the vaccine antigen enters the body, it is filtered through the lymph nodes where it is shown to B cells, part of the immune system. The goal of vaccination is to train B cells to produce specific antibodies targeted at the antigen.
B cells retaining the memory of how to do this persist in the body, so even if you come into contact with the real pathogen years later, there’s an immune task force ready to spring into action. Protection varies between vaccines, which is why boosters are sometimes required – but do you have to get your boosters in the same arm?
A team led by researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney, previously discovered that some memory B cells hang around in the lymph node closest to the site where a vaccine was administered. There, they interact with the resident macrophages – another type of immune cell.
Sophisticated imaging techniques have now revealed that when a booster vaccine is given in the same location, those macrophages are already primed to respond quickly. They present the antigen to the B cells, prompting them to start making high-quality antibodies in double-quick time.
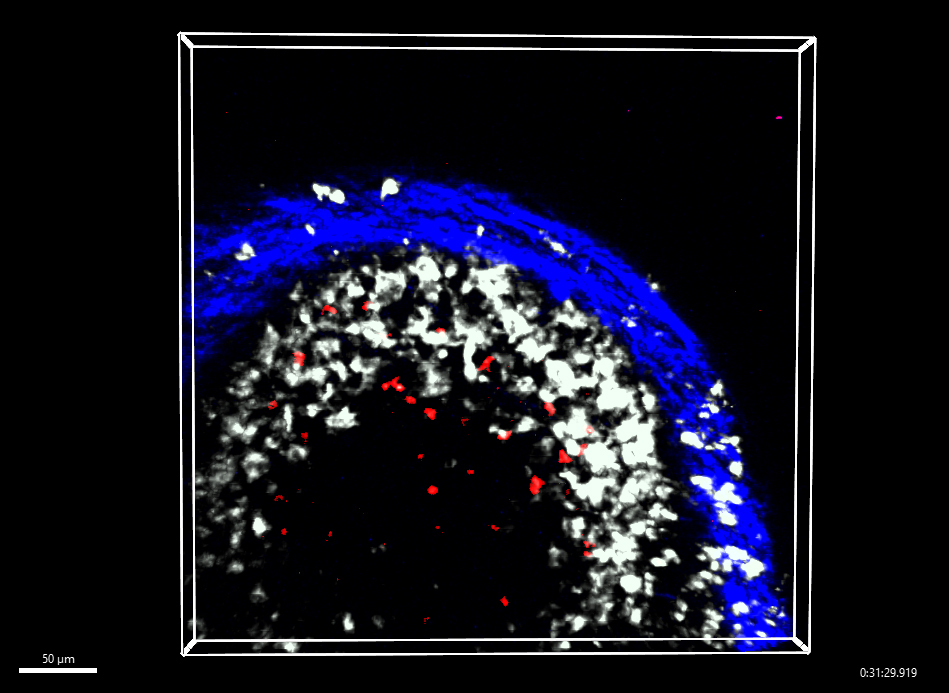
Here you can see the memory B cells in red interacting with the white macrophages inside the lymph node (blue border).
Image credit: Dr Rama Dhenni
“Macrophages are known to gobble up pathogens and clear away dead cells, but our research suggests the ones in the lymph nodes closest to the injection site also play a central role in orchestrating an effective vaccine response the next time around,” said co-first author Dr Rama Dhenni in a statement.
These results were first observed in mice, so the team was keen to see if the same was true in humans. They recruited 30 healthy volunteers who had not been exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the COVID-19 virus, and gave them a dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine.
mRNA vaccines work differently from many traditional vaccines. Rather than containing whole copies of SARS-CoV-2, they instead contain instructions – in the form of mRNA – that tell our cells how to make a key viral protein. Other than that, the principle is the same – our cells make the protein, and then the immune system prepares a response to it as described above.
After their initial shots, 20 of the participants received a booster in the same arm, while the other 10 had theirs in the opposite arm.
“Those who received both doses in the same arm produced neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 significantly faster – within the first week after the second dose,” explained co-first author Alexandra Carey-Hoppé.
“These antibodies from the same arm group, were also more effective against variants like Delta and Omicron. By four weeks, both groups had similar antibody levels, but that early protection could be crucial during an outbreak,” added co-senior author Dr Mee Ling Munier.
The authors stress that you shouldn’t worry if you’ve had doses of vaccines in both arms; but this knowledge could be very useful in the context of an emerging pandemic or disease outbreak, helping to get population immunity levels up as fast as possible.
“If we can understand how to replicate or enhance the interactions between memory B cells and these macrophages, we may be able to design next-generation vaccines that require fewer boosters,” said co-senior author Professor Tri Phan.
“This is a fundamental discovery in how the immune system organises itself to respond better to external threats – nature has come up with this brilliant system and we’re just now beginning to understand it.”
The study is published in the journal Cell.
Source Link: Vaccines And Boosters Work Best In The Same Arm, And We're Just Learning Why