Following years of activism from Indigenous communities and environmentalists, the removal of dams along the Klamath River is allowing water to flow freely once again, marking a new hope for the region’s iconic salmon.
The Klamath River, which trails for 414 kilometers (257 miles) between Oregon and northwestern California, was once the third-largest salmon-producing river on the West Coast. It supported a healthy population of Chinook salmon, coho salmon, and steelhead trout, which served as a vital source of nutrition for the Yurok, the Karuk, and other Indigenous tribal groups that live in the river basin.
However, the construction of PacifiCorp’s hydroelectric dams along the river between 1911 and 1962 led to a major decline in wild fish stocks. The dam effectively stopped the strong flows of water needed to “flush out” toxic algae, worms, and other organisms that can cause disease in fish.
Now, the dams are reaching the end of their lifetime, signaling an ideal time to remove them and attempt to revive the river’s once-thriving ecosystem.
The dams have caused severe headaches for the Yurok Tribe who had relied on the rivers for decades. Salmon from the Klamath River wasn’t just a key food source for the community but also played a significant role in their culture and identity.
After an especially severe die-off of Chinook salmon in 2002, Indigenous groups and environmentalists ramped up their efforts to push for the removal of the dams.
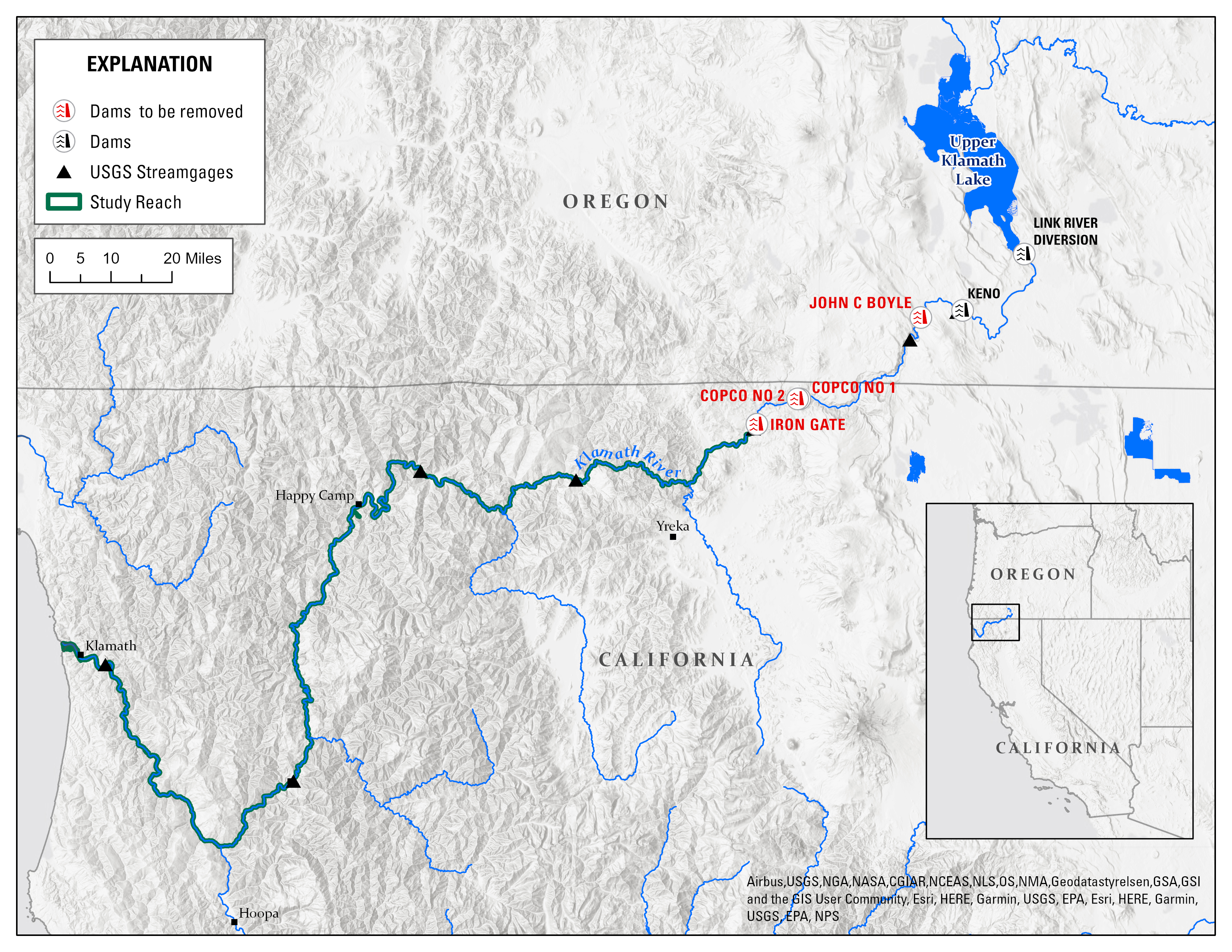
A map showing the Klamath River and its numerous dams.
Image credit: USGS; public domain
Against the odds, their effort paid off. In 2022, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission officially announced they would be decommissioning and removing the dams from the Lower Klamath Hydroelectric Project.
“It fills my heart to know that salmon will migrate through this river reach on their way to spawn in the upper basin,” Yurok Vice Chairman Frankie Myers said in a statement last year.
“For the last century, we have watched the dams suffocate the life out of the river and it has negatively impacted every member of our tribe,” Myers added.
The dam removal project is now reaching a key stage. As reported by the San Francisco Chronicle, water behind three of the dams was released last week, allowing water to flow freely through the Klamath River for the first time in a century.
“We’re now pulling the plug and throwing it away,” Myers told the newspaper.
“Not to get too mushy about it but being able to look at the river flow for the first time in more than 100 years, it’s incredibly important to us. It’s what we’ve been fighting for: to see the river for itself,” he added.
However, the river’s salmon will now face a new challenge: climate change. Recent years have seen record droughts and intense wildfire activity in this pocket of North America, which could hamper the recovery of wild fish populations.
While the dam removal is set to boost their numbers, the salmon of the Klamath River aren’t out of the woods yet.
Source Link: Water Is Freely Flowing Down The Klamath River For First Time In 100 Years